If you’ve majored in psychology and are wondering what your options are, the following list of potential careers in psychology might help. There are many careers in psychology; this isn’t an exhaustive list, though, as new specialisms keep popping up. We’ll also be briefly looking at careers in related fields that might make use of your psychology degree, as well as other sectors where your degree might be valuable.
There are two ways you can use this resource.
First, you can read every career option on our list. This might be useful if you have no clue what you want to do and need some inspiration about your future career in psychology, but it might take a while.
Second: you can use the links below to jump straight to a career that catches your eye. This will save time if you already have a rough idea of what psychology job you might want to do. We’ve helpfully put the links alphabetically so you can find the one you’re looking for quickly and easily.
|
Table Of Contents
show
What Do Psychologists Do?Individuals who delve into a career in psychology are often multifaceted in their roles. Whether operating from a lab, guiding students in a school, or directing their private practice, a unifying thread ties them all: a profound engagement with research. Psychologists are deeply committed to unraveling the intricacies of human behaviors and responses. Their quest is to decode the myriad factors—both internal and external—that shape our thoughts, emotions, and actions. Through rigorous research and exploration, psychologists seek to understand the foundational reasons underpinning our diverse human experiences and reactions. Why Pursue a Career in Psychology?
That being said, responsibilities vary. Psychologists may be hired to:
As you can see, there isn’t just one way to be a psychologist. Where Can You Get Hired as a Psychologist?Many different organizations may hire a psychologist to take on these responsibilities, including:
Psychologists also have another option: opening their practice. Depending on the type of psychology you have studied. How you want to serve your clients, your private practice may offer services to individuals who want to improve their mental health or corporations looking to improve how they treat their staff and motivate their leaders. |
Art Therapist
Art therapists encourage people to express themselves and their feelings through creative arts. You will need to be trained in a combination of psychotherapy and art and can work individually or as part of a group using a wide range of materials. Typical clients include:
- People who’ve had a traumatic brain injury (TBI)
- People who’ve experienced trauma
- Adults suffering from chronic or severe stress
- Children with disabilities
Aviation Psychologist
Aviation psychologists work for airlines, airports, and government agencies. Drawing on human behavior, typical duties might include:
- Evaluating prospective pilots and cabin crew
- Researching aviation safety
- Helping reconstruct aviation accidents
- Training flight crews in communication strategies and managing passengers with in-flight anxiety
- Counseling
Adolescent Psychologist
Adolescent psychologists typically work with young people between 12 – 18, although some work with younger children or young adults. This work requires an in-depth understanding of sociocultural and developmental factors specific to each age group. Work can be complex, challenging, and hopefully – rewarding - and may include:
- Abuse
- Autism
- Bullying
- Trauma
- Eating disorders
- Cognitive deficits
Advertising Psychologist
Advertising psychologists work with businesses and organizations. The role involves researching and analyzing consumer preferences and behavior and then advising the business to make its advertising efforts to promote a brand, service, or product as effectively as possible. Activities in this job might involve:
- Brand development strategy
- Script development
Analytical Psychologist
Analytical psychologists are interested in how our conscious and non-conscious beliefs and perceptions impact how we think and behave. The role involves aspects of psychoanalysis, and clients may need help with:
- Managing and coming to terms with chronic illness or disability
- Managing and understanding their emotions, such as stress, anxiety, fear, anger, or rage
Behavioral Psychologist
Behavior psychologists fall into 4 main categories: cognitive therapy, behavioral therapy, cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), and applied behavioral analysis (ABA).
Each therapeutic approach addresses any harmful thought processes, attitudes, and behaviors that prevent a person from having a happy, fulfilling life. The purpose of any behavioral psychologist, irrespective of approach, is to help people understand their thinking and behavior, offer tools and strategies to manage these and turn them into positive and helpful ways of thinking and behaving.
Behavioral Disorder Counselor
A Behavioral Disorder counselor works with people with behavioral disorders or issues that might negatively affect their relationships, work, and day-to-day functioning. You might be working with individuals who have:
- ADHD (Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder)
- OCD (Obsessive Compulsive Disorder)
- PTSD (Post Traumatic Stress Disorder)
- Eating disorders
- Substance abuse disorders
- Gambling
Biological Psychologist
Biological psychologists focus on the relationship between genetics, biological and physiological factors on human behavior and thought processes. Often this involves investigating and analyzing the differences between other species and human beings, so you are more likely to be carrying out animal studies in this field. If that makes you uncomfortable, this might not be your career.
Child Life Specialist
A child life specialist usually works within the pediatric department of a hospital. This role is about helping children under 18 - and their families - manage the experience of being hospitalized or having a chronic health condition. You can be involved at any stage or all of them. This means you could be helping a child and their family cope before, during, or after any treatment. This role is a mix of providing educational and emotional support, so you’ll need to know about medical terminology and what’s involved in hospital procedures, as well as having basic counseling and great communication skills.
Child Psychologist
Child psychologists are interested in the primary issues children and adolescents face, such as developmental milestones, educational and behavioral problems, social skills, and emotional issues. No day will likely be the same with such a broad spectrum of issues. Typical activities will vary depending on your area of expertise and whether you are in private practice or not, but may include:
- Administering a variety of psychological tests
- Offering therapy, such as CBT
- Systemic therapy, such as Functional Family therapy
- Involvement in developing Individual Education Plans (IEP)
Child Therapist
Child therapists usually work with children with complex needs who may have experienced abuse and trauma. This is an emotionally demanding role and may involve:
- Play therapy
- Family therapy
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
- Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR)
Clinical Psychologist
Clinical psychologists assess, diagnose, and treat clients suffering from various psychological, emotional, social, and behavioral problems. Clinical psychologists can do everything except prescribe medication; they are not classed as medical doctors. In this role, you may work in hospital settings, mental health clinics, or private practice. Most clinical psychologists will be educated to master level, with most having a Ph.D. You may work with people who have:
- Severe mental health, such as schizophrenia
- Emotional distress due to abuse, neglect, domestic abuse, and trauma
- Behavioral disorders, such as OCD and ADHD
- Learning disabilities
Criminal Psychologist
See Forensic Psychologist.
Cognitive Psychologist
Cognitive psychologists focus on understanding how the mind works, particularly concerning perception, memory, language development, attention, learning, and sensory processes. This role mainly involves research and teaching, although there is some opportunity to work in clinical settings helping people with cognitive problems related to age, brain injury, or developmental deficits. Becoming a cognitive psychologist is one of the most fascinating careers in psychology because you will learn how people think.
Community Psychologist
Community psychologists are part of a relatively new discipline that combines public health, sociology, social work, psychology, and ecology. This role focuses on understanding how people relate and interact as a community, emphasizing trying to develop strategies to combat community-level problems, such as teen pregnancy. You’ll likely be involved in carrying out research and working with local community leaders and members rather than providing help and support on an individual basis.
Consumer Psychologist
Consumer psychologists study the wants and needs of people to understand what influences them to purchase goods and services. They also analyze how family, friends, culture, and media messages affect consumer behavior. In this role, you might typically be involved in the following:
- Working with consumer focus groups
- Developing advertising and marketing campaigns
- Research on shopping and buying behavior
Cyberpsychologist
Cyberpsychology is another relatively new field investigating how online affects human behavior. In this role, you might research virtual reality, artificial intelligence, social media, online behavior, human-machine interaction, and technology addiction. As a Cyberpsychologist, your role will likely be more about research and analysis than interacting with individuals or groups of people.
Developmental Psychologist
Developmental psychologists specialize in human development and change. While you can be a generalist, it’s more likely that you’ll specialize and work with a specific age group, pediatric, adolescent, young adult, or the elderly. This is because each life stage poses different developmental milestones and issues. You could be working either in research or clinical or educational settings. Areas of particular interest include:
- Attachment theory
- Education
- Memory
Ecological Psychologist
Ecological psychologists are interested in understanding human behavior within the context of their environment. Largely a research-based role, you might be investigating microenvironments (such as the effect of immediate family) or macroenvironments (such as the effect of community and culture on behavior).
Educational Psychologist
Education psychologists focus on the various aspects of education, such as teaching strategies, learning processes and styles, language development, testing and assessments, and even behavioral issues. In this role, you’re most likely to work within an education setting to help students of any age fulfill their academic potential. However, you could end up in a more research role if this appeals to you. Typical responsibilities might include:
- Assessing and testing pupils
- Developing teaching programs
- Developing and delivering teaching strategies
- 1:1 work with children with behavioral problems
Engineering Psychologist
Engineering psychologists use their understanding of human behavior to help design and improve technology, consumer products, work settings, and living environments. You will likely be working within an academic setting or for a private organization. If you’re working for a business or organization, you could be working with or as part of one of these teams:
- Design
- Product Development
- Engineering
Evolutionary Psychologist
Evolutionary psychology is mostly a research role, investigating and analyzing how the brain and its cognitive processes have developed over time. You’ll need to be interested in biology, anthropology, and history. This is a specialized field with few jobs available, with most jobs being in academia.
Experimental Psychologist
Experimental psychologists carry out research. This can be across a huge range of subjects and specialisms. You may work in a research center, college, governmental agency, or private organization. This role typically involves the following activities:
- Planning an experiment
- Designing experiments
- Carrying out experiments
- Writing up reports/ submitting academic papers for publication
Forensic Psychologist
See also Criminal Psychologist.
Forensic psychologists focus on working within the judicial, family, and criminal law and the correctional system. While you might immediately think of being a psychological profiler – this is rarer than you think. This role has a lot in common with criminal psychology, as you could be working within the legal and judicial system, assessing criminal behavior, and providing court reports on the psychological functioning of criminals. You might also be involved in victim rights, child abuse cases, family conflict, and child custody cases.
Some forensic psychologists specialize in working inside correctional facilities, assessing, treating, and reporting on the psychological problems of inmates – not for the squeamish!
Geriatric Psychologist/ Geropsychologist
A Geriatric psychologist or Geropsychologist specializes in assessing and treating the elderly. This role can involve:
- Keeping older adults mentally and physically healthy
- Working with dementia
- Managing age-related illness and disability
- Loneliness
Health Psychologist

Health psychologists have a distinct focus on health and well-being. Unlike most other psychologists, the emphasis is not on psychological-related assessment or treatment. Instead, you will focus on how to help prevent illness and promote healthy behaviors, such as regular exercise, eating a balanced diet, and so on. In this role, you might work with governmental health agencies in hospitals, healthcare centers, and schools. Most of your work will involve educating people so that you might carry out activities such as:
- Developing health policy
- Developing hospital procedures
- Drafting health-related information such as leaflets
- Running health workshops on topics such as stopping smoking, eating healthily, and reducing stress
Human Factors Psychologist
Human Factors psychologists focus on human thought and behavior but also on weaknesses and strengths – both psychological and physical. Work in this field generally involves assessing and understanding how these human factors affect how we use and interact with our environment, tools, and workplace. Human factors psychology aims to ensure that products and services are designed to be safe, effective, and user-friendly.
Industrial/Organizational Psychologist
Industrial and organizational psychologists are interested in the physical workplace and workplace behavior, such as employer/employee interactions. This job is one of the highest-paid jobs in psychology due to its economic advantages to businesses. Organizational psychology has evolved from simply evaluating employees (and job applicants) to determine suitability to include a much wider range of tasks, including:
- Training employees
- Assessing employees
- Introducing processes and tools that improve productivity
- Involvement in HR and recruitment
Legal Psychologist
See also Forensic Psychologist.
Legal psychologist roles have some overlap with Forensic psychology. This is because both specialisms are involved in the judicial and criminal systems. In this role, you might work with a law firm or the district attorney's office. Most importantly, your responsibility will be that of a jury consultant and helping construct and vet jurors. Other responsibilities might be more administrative and involve working with city officials to develop policy and documentation on various societal issues, such as drunk driving.
Mathematical Psychologist
Mathematical psychologists may also be referred to as mathematical scientists. This is because this field focuses much more on the science of math to research quantifiable and measurable evidence about human behavior than a pure interest in psychology. This is a great choice if you love statistical analysis and numbers. As an exclusively research-based role, there is no chance of interacting or acting in a helping capacity with actual people.
Marriage Counselor
Marriage counselors work with couples (who don’t necessarily have to be married) experiencing relationship problems or where one partner has concerns about the other. You guide and advise couples who come to you for help. Typical work can involve:
- Couple therapy
- Family therapy
- Individual therapy
- Managing conflict
- Improving communication skills
Media Psychologist
Media psychology is a very specialized field that is still developing. Media psychologists explore the relationship between the media (TV, internet, radio) and human behavior. You might work for a private organization such as a tech or social media company. Topics of interest to media psychologists include:
- Effect of video games on socio-emotional development
- Effects of news media (including “fake news”)
- Effectiveness of advertising on different forms of media
- Impact of social media across all ages
Military Psychologist
See also Clinical Psychologist.
Military psychologists are most likely qualified clinical psychologists, and their role is largely the same, albeit when working with military personnel. Unlike many other career careers, as a military psychologist, you are more likely to be deployed anywhere in the world – including war zones or hostile environments.
Neuropsychologist
Neuropsychologists are specifically interested in the human brain, including cognition, traumatic brain injury (TBI), neurological conditions (Parkinson’s, Dementia, etc.), and mental health. Due to the broad nature of this work, neuropsychologists often specialize in a specific field, which can fall into either research or applied work. Typical work can therefore vary dramatically, but in an applied setting, tasks might include:
- Patient assessment
- Formulation
- Developing treatment plans
Occupational Health Psychologist
Occupational health psychologists focus on the impact of physical and mental well-being in the workplace. Although there’s a big emphasis on stress, occupational health can look at other things, such as specialist chairs for back problems, built-in breaks from computer screens, etc. This role is about reducing staff illness and time off work. Typical activities might include:
- Workplace assessments and suggesting workplace modifications
- Employee fitness assessments
Operational Psychologist
Operational psychologists usually work within governmental agencies and the military to help senior officials take accurate and appropriate combat and other operational actions. Activities may involve:
- Identifying operational risk
- Identifying security threats
- Advising on interrogation techniques
- Assessment of military personnel. Including analyzing personality traits
- Therapeutic support for trauma-related problems such as PTSD
Psychiatric Social Worker
Psychiatric social workers have a supportive role working with individuals and their families where there is a concern about the impact mental health problems have on the social and economic aspects of their lives, such as parenting capability, work, and personal relationships. The role is very similar to a traditional social worker, except they work exclusively with people diagnosed with mental illness. Often psychiatric social workers are the first line of defense and work much more closely with people and their families than most other psychologists. If you're looking for a fulfilling career in psychology, this may be one of the best.
Rehabilitation Psychologist
Rehabilitation psychologists focus on assessing, diagnosing, and treating individuals who need support. This could be because they have a chronic illness, long-term disability, physical injury, and even victims of domestic violence. This role involves working directly with people to determine their needs, creating a personalized treatment plan, and supporting them throughout. Typical activities in this role can include:
- Assessment
- Treatment delivery
- Counselling
- Coordinating services with other professionals, such as speech pathologists and occupational therapists
Social Psychologist

Social psychologists are interested in how individuals are affected by society, cultural influences, social policy, and even other people. This role can be largely academic, with an emphasis on research activities. However, social psychologists may also be employed in the private sector or by government agencies and help these organizations understand individual responses and behavior. Areas you could work in include:
- Health Science
- Political science
- Educational policy
- Public perception
Sports Psychologist
Sports psychologists focus on sports and athletics from a psychological perspective. An interest in sports is essential as you will specialize in understanding the factors that impact motivation and performance and how to reduce the psychological impact of injury on a sportsperson. As a sports psychologist, you can work in various settings, such as colleges, hospitals, and athletic centers, and even with state or national sports teams. Going down a research path is also possible if that appeals to you. Many high-schoolers look into this field to study if they are in sports and wish to follow their love into a well-paying psychology career.
Theoretical Psychologist
Theoretical psychologists can also be considered research psychologists. This role is about understanding the connection between psychology, philosophy, and theory. Most theoretical psychologists are employed in academic settings (which usually means you’ll also be teaching) and are involved in experiments to prove or disprove a given theory. Common topics of interest include:
- Ethics
- Phenomenology
- Cultural research
- Literary research
Traffic Psychologist
Traffic psychology is a newer area of psychology. Traffic psychologists apply theoretical principles to identify why drivers behave as they do. In this role, you might be involved in:
- Investigation links between driver behavior and road accidents
- Analyze traffic data
- Devise ways of improving traffic safety and preventing accidents
- Researching perceptions and attitudes towards public transport
Vocational Psychologist
Vocational psychologists are similar to career counselors. This could be your job if you’re interested in helping others discover what they want to do. Typical tasks might include:
- Evaluating individual skills and aptitudes
- Helping people prepare for interviews
- Guidance on how to qualify for a job
Psychiatrists and Related Careers
You might be wondering why psychiatrists are missing from our list. There’s a really good reason for this - psychiatrists differ from psychologists as they are medical doctors and can prescribe medication. Having a psychology degree won’t necessarily help you become a psychiatrist. You’ll need a medical degree above anything else.
Other sectors where psychology graduates can work:
- Finance
- Government
- Human Resources
- Interior Design
- Journalism
- Marketing/ PR
- Police
- Politics
- Teaching
- and lots more…
Using Psychology in Non-Psychologically Related Careers
Psychology, the study of human behavior and the mind isn't just for those in clinical or counseling roles. Its principles are universal and can be applied across a myriad of professions. Let's explore how psychology might be leveraged in careers that aren't primarily focused on psychology:
- Business and Marketing:
- Consumer Behavior: Understanding why consumers make certain choices can help businesses tailor their products or marketing strategies.
- Team Dynamics: Insights into group behavior can aid in creating more efficient and harmonious teams.
- Education:
- Learning Styles: Teachers can use psychology to identify and cater to various learning styles, optimizing education for every student.
- Behavior Management: Techniques grounded in psychological principles can help manage classroom behavior.
- Law and Criminal Justice:
- Jury Dynamics: Lawyers might use psychological principles to understand jury dynamics or how to present their case effectively.
- Criminal Behavior: Understanding the underlying factors of criminal behavior can be useful in law enforcement and rehabilitation efforts.
- Healthcare (Outside of Mental Health):
- Patient Communication: Doctors and nurses can use psychological techniques to communicate effectively with patients, ensuring they understand their medical conditions and treatment plans.
- Stress Management: Healthcare professionals can integrate psychological principles to help patients manage stress or anxiety related to their health conditions.
- Arts and Entertainment:
- Audience Engagement: Filmmakers, writers, and artists can leverage psychology to craft narratives that resonate deeply with audiences.
- Performance Anxiety: Performers can utilize psychological techniques to overcome stage fright or performance-related anxieties.
- Human Resources:
- Conflict Resolution: HR professionals can employ psychological methods to mediate disputes and maintain a positive work environment.
- Recruitment: Understanding what motivates individuals can aid in recruiting the right talent for the right roles.
- Design and Architecture:
- User Experience (UX): Designers can employ psychological principles to understand how users interact with spaces or digital products, enhancing functionality and user satisfaction.
- Environmental Psychology: Architects and urban planners can use psychology to design spaces that promote well-being and facilitate social interaction.
- Sales and Retail:
- Building Rapport: Salespeople can employ psychological techniques to build customer trust and rapport, increasing sales and fostering loyalty.
- Understanding Needs: By gauging a customer's emotional and psychological state, sales representatives can better cater to their needs.
In essence, the knowledge of psychology is versatile. Regardless of the primary focus of a profession, understanding human behavior, emotions, and cognition can enhance efficiency, effectiveness, and overall success in that field.
Things to think about when choosing a career in psychology
Hopefully, you’re now feeling reassured that there’s a great career in psychology for you. But before you rush headlong into a decision, it might be a good idea to take a few minutes to think about the following:
- Does the career you’re looking at suit your personality?
- Would you prefer to work autonomously or as part of a team?
- Do you want to help people directly, or would you prefer to work behind the scenes?
- Are you good with facts and figures?
- Do you enjoy writing, and are you good at it?
- Do you want to work with children and young people?
- What level of education can you commit to?
- Does the average salary for the job feel ok to you?
- How much do you want to earn?
- Are you interested in the typical daily tasks of the role?
- What environment do you want to work in?
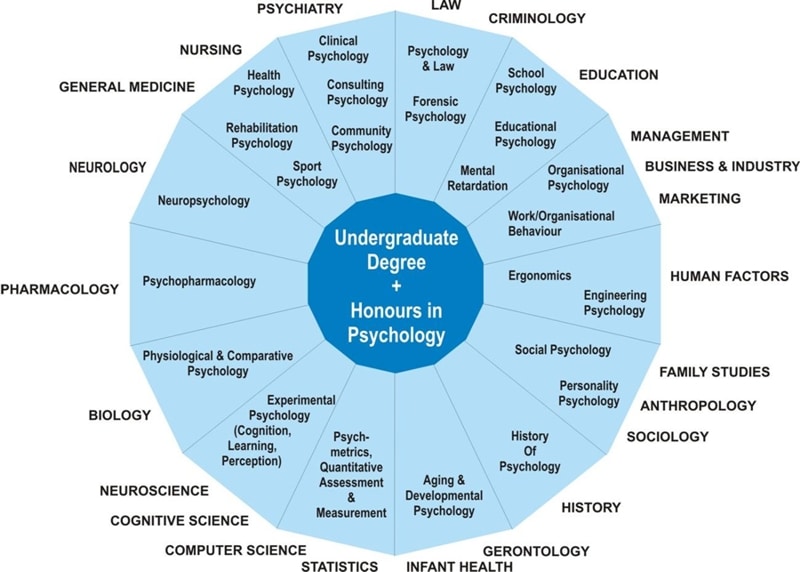
fPsychology is a massive field with many sub-disciplines and specialties, so the sooner you start thinking about your career path, the better. You can start by researching the possible careers in psychology that interest you and taking the time to think about what that job might be like daily. Good luck!
