A 2002 empirical survey endorsed by the American Psychological Association (APA) ranked Freud as the third most eminent psychologist of the 20th century.
Who Is Sigmund Freud?
Sigmund Freud was an Austrian neurologist and the founding father of psychoanalysis. He believed that childhood experiences can impact adult life and help to shape our personality. Despite proposing a number of controversial theories throughout his career, Freud's influence on the field of psychology is profound.
Sigmund Freud's Family Background
Sigmund (originally Sigismund) Freud was born on May 6, 1856, in the small Moravian town of Freiberg (now Pribor, Czech Republic). He was the eldest of eight children born to Jewish parents Jakob Freud and Amalia Nathansohn. Freud’s father worked as a wool merchant and had two adult sons from a previous marriage. At the time of Freud’s birth, the family was relatively poor and lived in a single rented room. Due to mounting financial struggles, they left Freiberg in 1859, and eventually settled in Vienna when Freud was four years old.
Childhood
Freud was taught to read and write by his mother and displayed superior intellectual ability from an early age. He loved literature and began reading works by Shakespeare when he was eight years old. He had a flair for languages, and learned to speak Latin, Greek, English and French as a child. He also taught himself Spanish and Italian.
Freud had a close, positive relationship with his mother and is said to have been her favorite child. He was given a bedroom for himself so he could focus on his studies, a privilege none of his other siblings received. His mother would often serve him his meals in his room.
Early Schooling
Freud’s first exposure to formal education came in 1865 when he entered a prominent high school at age nine—a year earlier than most of his peers. He was an excellent student and was constantly at the top of his class. He graduated with honors at age 17.
Educational Background
In 1873, Freud enrolled at the University of Vienna to study medicine. He completed his studies and earned his MD in 1881. Between 1882 and 1885, Freud worked in various departments at the Vienna General Hospital, including the Department of Psychiatry. He was appointed as a Privatdozent (lecturer) at the University of Vienna in 1885. In that same year, he received a grant to study in Paris under neurologist Jean-Martin Charcot, who trained him in the use of hypnosis to treat the condition then known as hysteria.
Upon his return to Vienna, Freud began his private practice, specializing in nervous and brain disorders. During the 1890’s, he became dissatisfied with hypnosis as a treatment method for hysteria and began focusing more on an approach he learned previously from respected Viennese physician, Josef Breuer. While Freud was still in medical school, Breuer began treating a young woman pseudonymously called Anna O. for symptoms of hysteria. Breuer found that if he hypnotized the woman and asked her to recall events that occurred around the time a particular symptom first appeared, that symptom would disappear.
Free Association
Freud adapted Breuer’s method by having patients lie on a couch with their eyes closed, and encouraging them to talk freely about the first time they experienced a particular symptom. Unlike Breuer, Freud did not hypnotize his patients but found this method—which he termed free association—to be quite effective. Freud later coined the term ‘psychoanalysis’ to describe his approach to treatment, as well as the theory underlying his approach.
In 1902, Freud and a small group of scholars formed the first organized group of psychoanalysts, which was called the Wednesday Psychological Society (later known as the Vienna Psychoanalytic Society). That same year, he was promoted to the rank of full professor at the University of Vienna, a position which he held until 1938.
Freud's Theory of Psychoanalysis
Psychoanalysis is both a theory that attempts to explain human behavior and a form of talk therapy. Freud believed that childhood experiences help to shape one’s personality and can impact a person when he or she becomes an adult. The goal of psychoanalysis is to release repressed or pent up memories and emotions so that the individual in treatment can heal. This form of therapy involves bringing events that are in the unconscious or the subconscious to the conscious.
Freud developed psychoanalysis over the course of several years. As the theory evolved, it eventually covered a number of different concepts and mechanisms. To get a better understanding of what is involved in psychoanalysis and how the theory developed, it may be best to start with Freud’s view of the human mind.
Freud’s Model of the Human Mind
One of Freud’s most significant contributions to psychology was his model of the human mind. He believed the mind was divided into three regions:
- The Conscious - this is the part of the human mind that contains current thoughts and feelings. Anything you are aware of and are focusing on right now is in the conscious part of your mind.
- The Preconscious (also called the Subconscious) - this region of your mind is home to emotions and experiences that you are not currently aware of, but you can easily retrieve them from memory.
- The Unconscious - this is the largest and deepest level of your mind and it contains all the instinctual desires, primitive wishes, hopes, and memories that are outside of your awareness. According to Freud, the things in your unconscious play a major role in driving your behavior. As mentioned before, psychoanalysis aims to bring unresolved material from your unconscious into your awareness so that you can process them fully and heal.
Freud later suggested that human personality was also divided into three major categories. These are:
- The Id - this is the most primitive part of your personality and it focuses on satisfying your most basic urges and instincts. The id develops during the early stages of infancy. It resides in your unconscious mind and is the source of libidinal energy. It is composed of two biological drives called eros (this is your instinct to survive) and thanatos (this is your instinct to destroy). Eros helps you to survive by directing processes such as eating, breathing, and sex which are essential for maintaining life. As eros is stronger than thanatos, people tend to have a stronger drive to live than self-destruct. When thanatos is directed outward to other people, it may be interpreted as aggression or violence.
- The Ego - this part of your personality deals with reality. It ensures that the basic urges and instincts of the id are satisfied in ways that are safe, realistic, and socially acceptable. Freud believed that the ego develops from the id during the later stages of infancy. The ego resides in your conscious, subconscious, and unconscious mind.
- The Superego -- this part of your personality develops during childhood and focuses on morality and higher principles. It contains all of the standards and morals you have learned from your parents, family members, and wider society. The superego encourages social responsibility. It resides in your conscious, subconscious, and unconscious mind.
Pleasure Principle
According to Freud, the id, ego, and superego interact to create complex human behavior. How is that possible? Consider the id, which is driven by the pleasure principle and seeks instant gratification for primitive urges such as hunger and thirst. The id is vital for infant survival as it ensures the baby’s needs are met quickly. As only the id is present during the early stages of infancy, the baby will cry until its primitive needs are satisfied. There is simply no point in trying to negotiate a later feeding time with a hungry baby.
As the baby grows older though, he may realize that getting all his needs met immediately may not be realistic or socially acceptable. For example, he may get in trouble if he gets hungry and decides to eat a box of cookies before dinner. Freud claimed that the id tries to resolve this tension by using primary process thinking. This involves forming a mental image of the desired object (in this case it would be cookies or another type of food) which helps to satisfy the primitive need temporarily.
The ego develops from the id during the latter part of infancy and operates on the reality principle. It tries to satisfy the desires of the id in a socially appropriate way. This means the child will weigh the pros and cons of a particular behavior instead of acting impulsively. In this case, a hungry child who is stuck in class may think about pizza (primary process thinking) until he finally gets the opportunity to eat during his lunch break and satisfy his desire in a way that is socially acceptable.
The superego is the last part of personality to develop. Freud claimed that the superego begins to emerge when an individual is about five years old. The superego contains a person’s sense of right and wrong, and it holds all the ideals and moral standards that have been learned over time. It provides the guidelines for making decisions.
The goal of the superego is perfect behavior. As it wants the individual to behave in a civilized manner, it works to restrict the unacceptable desires of the id and tries to make the ego act on standards that are idealistic rather than realistic.
Freud believed that a good balance between id, ego, and superego results in a healthy personality. If someone has an id that is too dominant, he may develop into an adult that is impulsive or uncontrollable. As such a person wants all his desires to be satisfied right away, he may be more likely to engage in criminal activity than the average person. On the other hand, an individual with a dominant superego may be extremely moralistic and judgmental. As a result, this individual may hold himself or other people to standards that are unreachable.
Defense Mechanisms
The term “defense mechanism” was first used by Freud in his psychoanalytic theory. According to Freud, the id, ego, and superego are in constant conflict with each other because each part of your personality has its own goal. A defense mechanism is a strategy used by the ego to protect against anxiety from unacceptable thoughts and feelings. It is an unconscious response that safeguards the individual from emotions or experiences that are too difficult to manage right now. In some cases, one or more defense mechanisms may prevent unacceptable thoughts and impulses from entering the conscious mind.
Common types of defense mechanisms include:
Repression - the ego pushes disturbing thoughts out of consciousness and prevents them from coming back into the conscious mind. For example, a person who experienced sexual abuse as a child may have repressed memories of the abuse.
Denial - overwhelming external events are blocked from awareness so that the individual refuses to believe or is not aware of what is currently happening. For example, people who are addicted to alcohol may refuse to believe that they have a drinking problem.
Rationalization - the individual explains difficult feelings or unacceptable behavior in a rational or logical manner while avoiding the real reason for the feelings or behavior. For example, a student who fails a test may reason that the instructor did a poor job in teaching the topic.
Displacement - the individual satisfies an urge or impulse by using a substitute object in a way that is socially inappropriate. For example, a man who is upset with his boss may come home and abuse his partner.
Sublimation - the individual satisfies an urge or impulse by using a substitute object in a way that is socially acceptable. For example, an athlete who is jeered by the crowd may use his emotions to raise his performance during the game.
Projection - the ego takes unacceptable thoughts or feelings and ascribes them to other people. For example, you may hate your teacher but you know these feelings are socially inappropriate. So you convince yourself that it is your teacher who hates you.
Regression - the individual moves backward in psychological development in order to cope with stress. For example, an adult who is stressed out at work may start throwing tantrums like a child.
The 5 Stages of Psychosexual Development
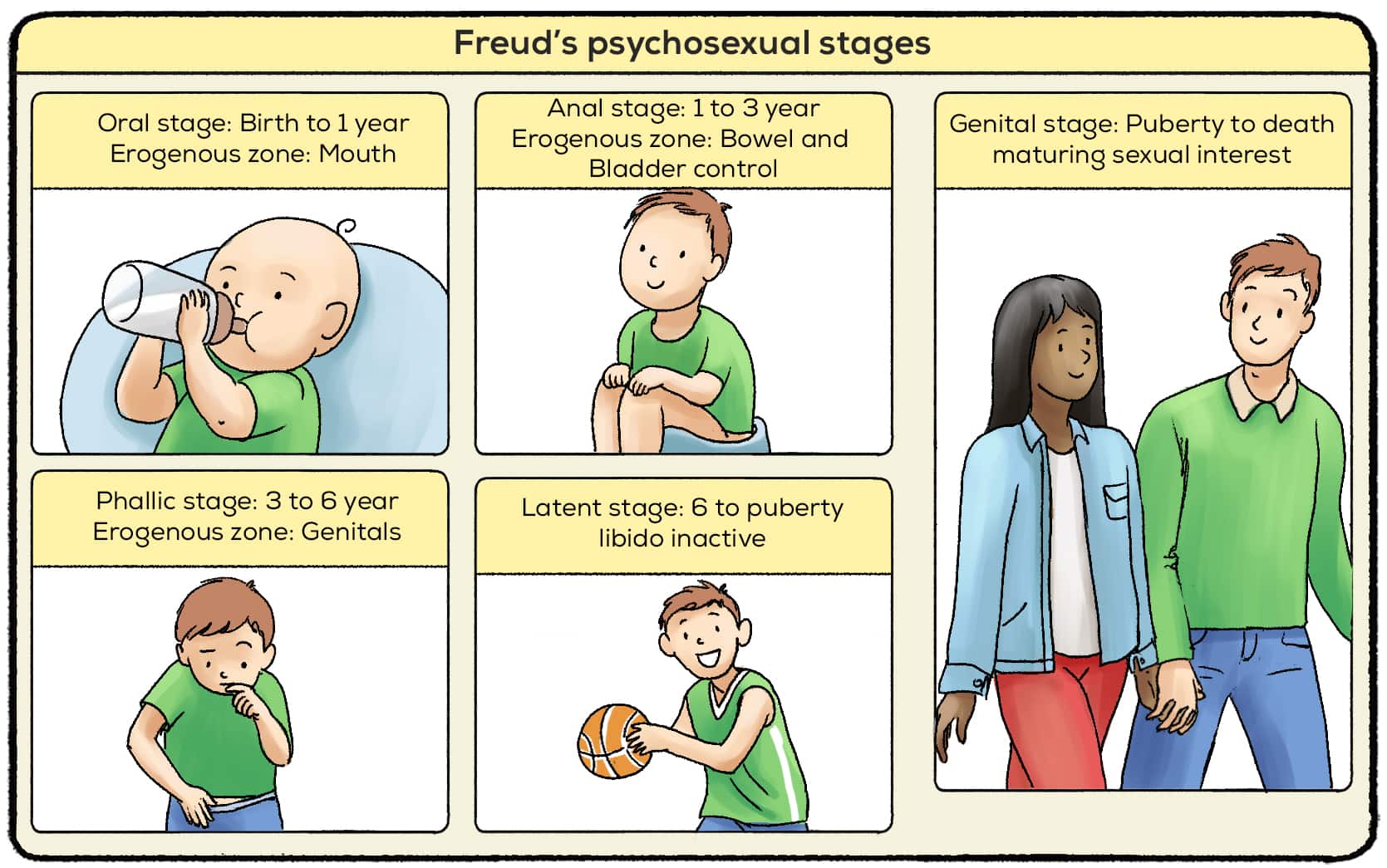
Freud suggested that children develop through five distinct stages of psychosexual development. He believed that children focus on a different body part as a source of pleasure in each stage. This is one of Freud’s most well-known and controversial theories. The five stages he proposed include:
- The Oral Stage (birth to 18 months) - the child seeks pleasure from the mouth (for example, sucking or feeding)
- The Anal Stage (18 months to 3 years) - the child seeks pleasure from the anus (for example, expelling or withholding feces)
- The Phallic Stage (3-6 years) - the child seeks pleasure from the penis or clitoris (for example, masturbation)
- The Latent Stage (6 years to puberty) - little libidinal energy is present as the child has no sexual motivation
- The Genital Stage (puberty to adulthood) - the child seeks pleasure from the penis or vagina (for example, sexual intercourse).
Oedipal Complex
Freud also proposed that an Oedipal complex occurs during the phallic stage when children are roughly 3-6 years old. He claimed that children in this stage of development have an unconscious desire for their opposite-sex parent and feel jealous of their same-sex parent.
The Oedipal complex manifests as either an Oedipus complex in boys or an Electra complex in girls. According to Freud, a young boy will develop an Oedipus complex, become sexually attracted to his mother and view his father as a rival. As his mother shows affection for his father, the boy fantasizes about getting rid of his father and taking his place. However, the boy also develops a fear that his father will castrate him (castration anxiety) so he begins to identify with his father and adopt his attitudes, behaviors, roles, and values. This eventually results in the father becoming a role model for the boy as the boy develops his superego and learns his roles as a male in society.
Penis Envy
Freud claimed that a young girl in the phallic stage will develop an Oedipal complex, become sexually attracted to her father, and treat her mother with hostility. The complex begins when the girl realizes that she does not have a penis and develops “penis envy.” She also blames her mother for her castration. However, fear of losing her mother’s love moves the girl to identify with her mother and adopt her attitudes, behaviors, roles, and values. This leads to the development of the girl’s superego as she learns her roles as a female in society.
Interestingly (and controversially), Freud suggested that the identification of a girl with her mother is less complete than the identification of a boy with his father. As a result, he claimed that the female superego is weaker and less developed than the male superego.
Freud believed that an individual must successfully complete each of the five psychosexual stages in order to develop into a healthy adult. If there is a conflict during any stage that remains unresolved, the individual may become stuck at that stage of development. For example, children who did not successfully complete the oral stage may demonstrate an excessive reliance on oral behaviors such as biting fingernails, eating, or smoking when they become adults.
Dream Analysis and Interpretation
Freud described dreams as “the royal road to the unconscious.” He believed that analyzing a person’s dreams could provide much insight into the thoughts, feelings, and memories that are buried deep within the mind. Freud viewed dreams as a way to see how the unconscious mind functions. He also used dreams to take a peek at what inappropriate thoughts lay outside of a person’s awareness.
Freud believed that the content in dreams could be separated into two categories called manifest content and latent content. Manifest content refers to all the images, sounds, and events the dreamer remembers once he awakens. Latent content refers to the symbolic meaning or underlying wish that is hidden in the dream.
According to Freudian theory, the main purpose of dreams is to fulfill wishes. Freud believed that dreams change forbidden desires into less threatening forms. This transformation takes place via condensation (joining two or more ideas together), displacement (changing the person or thing we are concerned about into someone or something else), and secondary elaboration (putting all the pieces together to form a coherent narrative).When this is done, the anxiety caused by the forbidden desire is significantly reduced in the dream.
Applications of Psychoanalysis
There are three main applications of psychoanalysis. It is used to:
- Explore the human mind
- Explain human behavior
- Treat psychological or emotional issues during talk therapy
Psychoanalysis helps people in treatment to better understand the unconscious forces that influence their current thoughts, feelings, and behaviors. This approach often involves eliciting emotional responses and helping individuals to overcome negative defense mechanisms. Psychoanalysis also teaches coping techniques so that people can address problems that arise in the future rather than fall back on unhealthy defenses. Individuals in therapy develop deep personal insight and learn how to deal with feelings that are difficult to process.
Although fewer therapists currently use psychoanalysis to explore human behavior or diagnose and treat mental health concerns, the approach is still well-known and hotly debated in the field of psychology. Freud’s work also influenced many younger psychologists who would help to develop the field, including Carl Jung, Erik Erikson, Alfred Adler, and Anna Freud.
Criticisms of Psychoanalysis
One of the major criticisms of psychoanalysis is that the theory is highly unscientific. While Freud suggested explanations for human behavior, he was unable to predict behavior because his methods were not based on objective measurements. Freud developed the majority of his theories while working with a small sample of people. As a result, his theories may not be applicable to the wider population.
Some people who need mental health counseling may avoid psychoanalysis because it can be a very intense and personal treatment approach. Critics argue that the approach is too time-consuming (treatment may last for years), too costly, and is generally ineffective. Notable researchers such as Karl Popper and Noam Chomsky have repeatedly claimed that psychoanalysis is not based on empirical evidence. Some critics have suggested that Freud may have focused on information that supported his theories and ignored data that did not fit.
Sigmund Freud's Books, Awards, and Accomplishments
Sigmund Freud was a prolific writer and published a number of books on his theories. Some of his most important works include:
- The Interpretation of Dreams, 1899
- The Psychopathology of Everyday Life, 1904
- Jokes and Their Relation to the Unconscious, 1905
- Three Essays on the Theory of Sexuality, 1905
- Five Lectures on Psycho-Analysis, 1910
- Introductory Lectures on Psycho-Analysis, 1917
- Beyond the Pleasure Principle, 1920
- The Ego and the Id, 1923
- Inhibitions, Symptoms, and Anxiety, 1926
- The Future of an Illusion, 1927
- Civilization and Its Discontents, 1930
- New Introductory Lectures on Psycho-Analysis, 1933
Personal Life
In 1886, Freud married Martha Bernays after a four-year engagement and the couple had six children—three boys and three girls. One of their daughters, Anna, later became a famous child psychoanalyst and was instrumental in leading the Freudian movement after her father’s death.
Though Jewish by birth, Freud did not practice Judaism as an adult. He developed an addiction to nicotine at age 24 and smoked roughly 20 cigars a day. He tried several times to quit but was unsuccessful. He was diagnosed with cancer of the palate and jaw at 67 years of age, resulting in a series of over 30 operations. He experienced chronic pain during the last 16 years of his life.
Following Nazi occupation of Austria in 1938, Freud fled Vienna, taking his wife and daughter, Anna, with him. The last 16 months of his life were spent in London, where he died on September 23, 1939, at 83 years of age.
References
American Psychological Association. (2002). Eminent psychologists of the 20th century. Retrieved from https://www.apa.org/monitor/julaug02/eminent
Hergenhahn, B. R. (2009). An introduction to the history of psychology (6th ed.). Belmont, CA: Wadsworth.
Rudnytsky, P. L. (2002). Freud, Sigmund. (1856-1939). In E. Erwin (Ed.), The Freud encyclopedia: Theory, therapy, and culture. New York: Routledge.
Sheehy, N. (2004). Fifty key thinkers in psychology. New York: Routledge.
Sigmund Freud (1856-1939). (n.d.). Retrieved from https://www.bbc.co.uk/history/historic_figures/freud_sigmund.shtml
