Sheep. Complicit. Doormat. There are a lot of negative connotations associated with conformity, especially in the United States. Individualist societies push back on "going along with what everyone is doing." And yet, we conform more than we think. According to studies like the Asch Line Study, humans have a natural tendency to conform.
The Asch Line Study is one of the most well-known experiments in modern psychology, but it's not without its faults. Keep reading to learn about how the Asch Line Study worked, its criticisms, and similar experiments!
How Did the Asch Line Study Work?
In his famous “Line Experiment”, Asch showed his subjects a picture of a vertical line followed by three lines of different lengths, one of which was obviously the same length as the first one. He then asked subjects to identify which line was the same length as the first line.
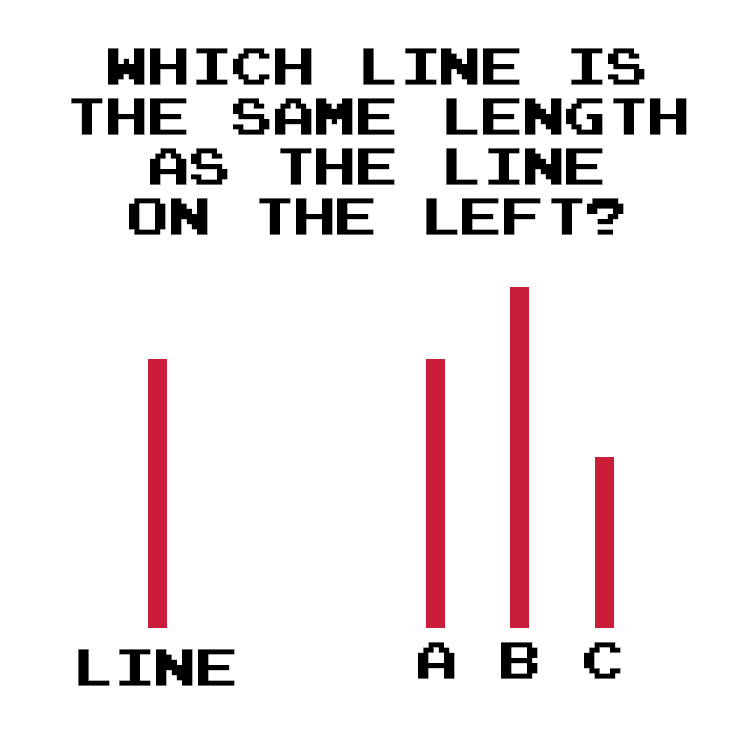
Solomon Asch used 123 male college students as his subjects, and told them that his experiment was simply a ‘vision test’. For his control group, Asch just had his subjects go through his 18 questions on their own.
However, for his experimental group, he had his subjects answer each of the same 18 questions in a group of around a dozen people, where the first 11 people intentionally said obviously incorrect answers one after another, with the final respondee being the actual subject of the experiment.
Who was Solomon Asch?
Solomon E. Asch was a pioneer in social psychology. He was born in Poland in 1907 and moved to the United States in 1920. Asch received his Ph.D. from Columbia University in 1932 and went on to perform some famous psychological experiments about conformity in the 1950s.
One of these studies is known as the “Asch Line Experiment”, where he found evidence supporting the idea that humans will conform to and accept the ideas of others around them, even if those ideas are obviously false. This study is one of the most influential studies in social psychology.
Findings of Asch's Conformity Study
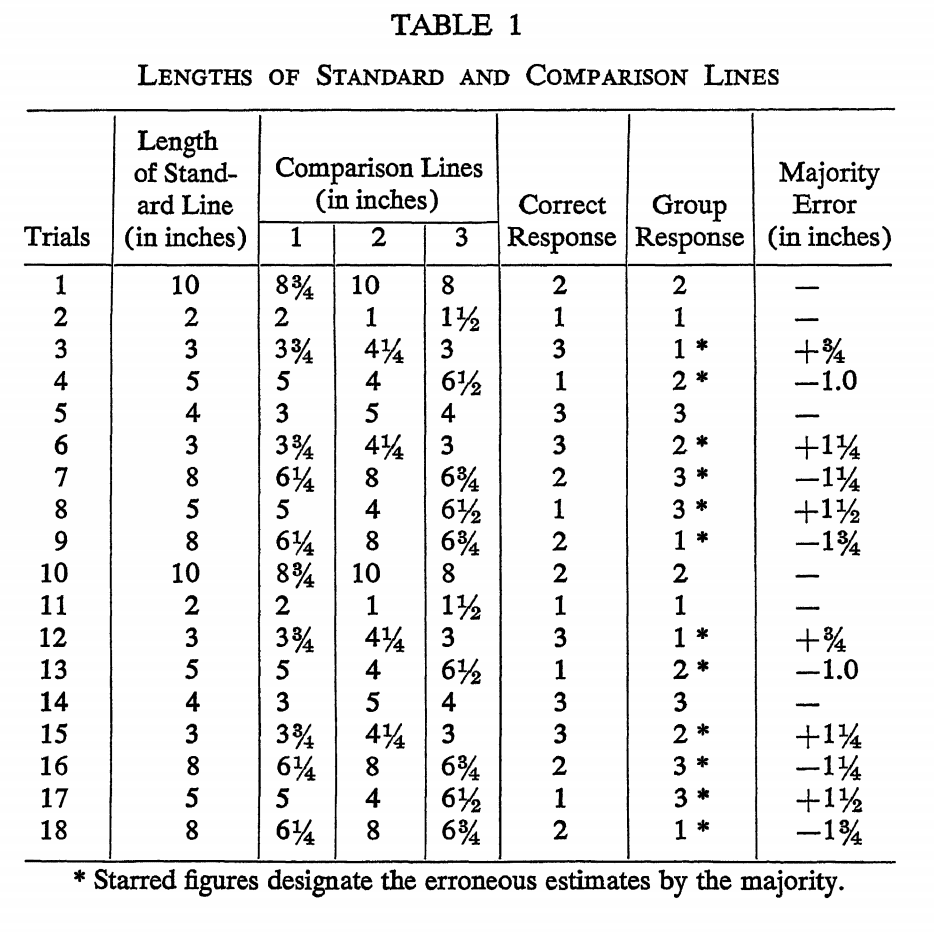
Asch found that his subjects indeed were more likely to give a false response after the other members of their group (the actors) gave false responses. As shown in this ‘Table 1’ from his experiment, during 18 trials, the ‘Majority Error’ column shows no error when the group response was the correct response, such as in Trial #1.
However, when the entire group intentionally gave a false answer (these situations are designated with an * under the “Group Response” column), the ‘Majority Error’ did exist and was slanted toward the opinion of the group.
For example, if the group answered with a line that was too long, such as in Trial #3, the ‘Majority Error’ column shows that the subjects generally estimated the line to be longer than it really was (denoted with a ‘+’), and vice-versa for when the group answered with a line that was too short, such as in Trial #4.
As for his control group, Asch found that people generally said the correct answer when they did not have a group of actors saying answers before them.
Interviewing the Participants
After the experiment, Asch revealed the true experiment to his subjects and interviewed them. Some subjects had become very agitated during the experiment, wondering why they kept disagreeing with the group. When the group pressed one particular subject on why he thought that he was correct and the entire group was wrong, he replied defiantly, exclaiming: “You're probably right, but you may be wrong!”
Other subjects admitted during the interview that they changed their answers after hearing others in their group reply differently. One was recorded saying, “If I’d been the first I probably would have responded differently.” Another subject admitted, “...at times I had the feeling: 'to heck with it, I'll go along with the rest.' "
Conclusions from the Asch Line Study
Asch found that his subjects often changed their answers when they heard the rest of the group unanimously giving a different response.
After the interviews, Asch concluded in his study that his subjects conformed to the opinions of the group for three different reasons:
Distortion of perception due to the stress of group pressure: This group of subjects always agreed with the group and said during the interview that they wholeheartedly believed that their obviously incorrect answers were correct. Asch concluded that the stress of group pressure had distorted their perception.
Distortion of judgment: This was the most common outcome, where subjects assumed that their individual answers were incorrect after seeing the rest of the group answer differently, so they changed their answer to align with the group.
Distortion of action: These subjects never doubted that they were correct and the group was wrong, but out of fear of being perceived as different, they suppressed their opinions and intentionally lied when it was their turn to give an answer.
Asch Line Study vs. Milgram Experiment
Both the Asch Line Study and the Milgram Experiment look at conformity, obedience, and the negative effects of going along with the majority opinion. Those negative effects are slightly awkward, like in the Asch Line Study, or dangerous, like in the Milgram Experiment. Both experiments were conducted in the Post-WWII world as a response to the conformity that was required for Nazi Germany to gain power. The premise of Asch's study was not nearly as dramatic. Milgram's was.
To test conformity, Milgram and his researchers instructed participants to press a button. Participants believed that the buttons would shock another "participant" in a chair, who was really an actor. (No one was shocked.) The study continued as long as participants continued to shock the participant at increasingly dangerous levels. The participants knew that they could cause serious harm to the person in the chair. Yet, many obeyed.
Further Experiments and Variations
Solomon Asch didn't just conduct one experiment and move on. He replicated his experiment with new factors, including:
- Changing the size of the actor group
- Switching to a non-unanimous actor group
- Having a unanimous actor group, except for one actor who sticks to the correct response no matter what the group or subject says
- Instructing the one actor who gives the correct response come in late
- Having one actor decide to change their answer from the group’s answer to the subject’s answer
There are also many reproductions and replications of this study online. Not all of them come to the same conclusions! Read through the following texts to get a sense of how other psychologists approached this subject:
- Larsen, K. S. (1990). The Asch conformity experiment: Replication and transhistorical comparisons. Journal of Social Behavior & Personality, 5(4), 163–168.
- Mori K, Arai M. No need to fake it: reproduction of the Asch experiment without confederates. Int J Psychol. 2010 Oct 1;45(5):390-7. doi: 10.1080/00207591003774485. PMID: 22044061.
- UKEssays. (November 2018). A Replication of Solomon Asch’s Conformity Studies. Retrieved from https://www.ukessays.com/essays/psychology/a-replication-of-solomon-aschs-conformity-studies.php?vref=1
Why Is The Asch Line Study Ethnocentric? And Other Criticisms
One big issue with the Asch line study is that the subjects were all white male college students between the ages of 17 and 25, with a mean age of 20. Since the experiment only shows results for this small and specific group of people, it alone cannot be applied to other groups such as women or older men.
Experimenter Bias in the Asch Line Study
Only choosing subjects from one demographic is a form of Experimenter Bias. Of course, researchers can use one demographic if they are specifically studying that demographic. But Asch was not just looking at young, white men. If he had expanded his research to include more participants, he may have produced different answers.
We assume Asch did not go about his study with the intention of being biased. That's the tricky thing about biases. They sneak up on us! Even the way that we share information about psychology research is the result of bias. Reporter bias is the tendency to highlight certain studies due to their results. The Asch Line Study produced fascinating results. Therefore, psychology professors, reporters, and students find it fascinating and continue to share this concept. They don't always share the full story, though.
Did you know that 95% of the participants actually defied the majority at least once during the experiment? Most textbooks don't report that. Nor did they report that the interviewees knew that they were right all along! Leaving out this key information is not Asch's fault. But it should give you, a psychology student, some pause. One thing that we should take away from this study is that we have a natural tendency to conform. This tendency also takes place when we draw conclusions from famous studies! Be critical as you learn about these famous studies and look to the source if possible.
Further Criticisms of the Asch Line Study
Does the Asch Line Study stand the test of time? Not exactly. If we look at what was happening in 1950s society, we can see why Asch got his results. Young white men in the early 1950s may have responded differently to this experiment than young white men would today. In the United States, which is where this experiment was performed, the mid-1950s was a historic turning point in terms of rejecting conformity. Youth were pushing toward a more free-thinking society. This experiment was performed right around the time that the movement was just starting to blossom, so the subjects had not grown up in the middle of this new anti-conformist movement. Had Asch performed this experiment a decade later with youth who more highly valued free-thinking, he may have come across very different results.
Another thing to note is that, at least in the United States, education has evolved with this movement of encouraging free-thinking. Teachers today tell students to question everything, and many schools reject ideas of conformity. This could once again mean that, if done again today, Asch would have found very different results with this experiment.
Another problem with this experiment is that, since subjects were not told it was a psychological experiment until after it was over, subjects may have gone through emotional and psychological pain during what they thought was just a simple ‘vision test’.
Finally, it’s good to remember that the ‘Asch Line Experiment’ is just that: an experiment where people looked at lines. This can be hard to apply to other situations because humans in group settings are rarely faced with questions that have one such obvious and clear answer, as was the case in this experiment.
