Are you looking to remember information more effectively? Share your message and make it stick! You've got to learn about the Von Restorff Effect!
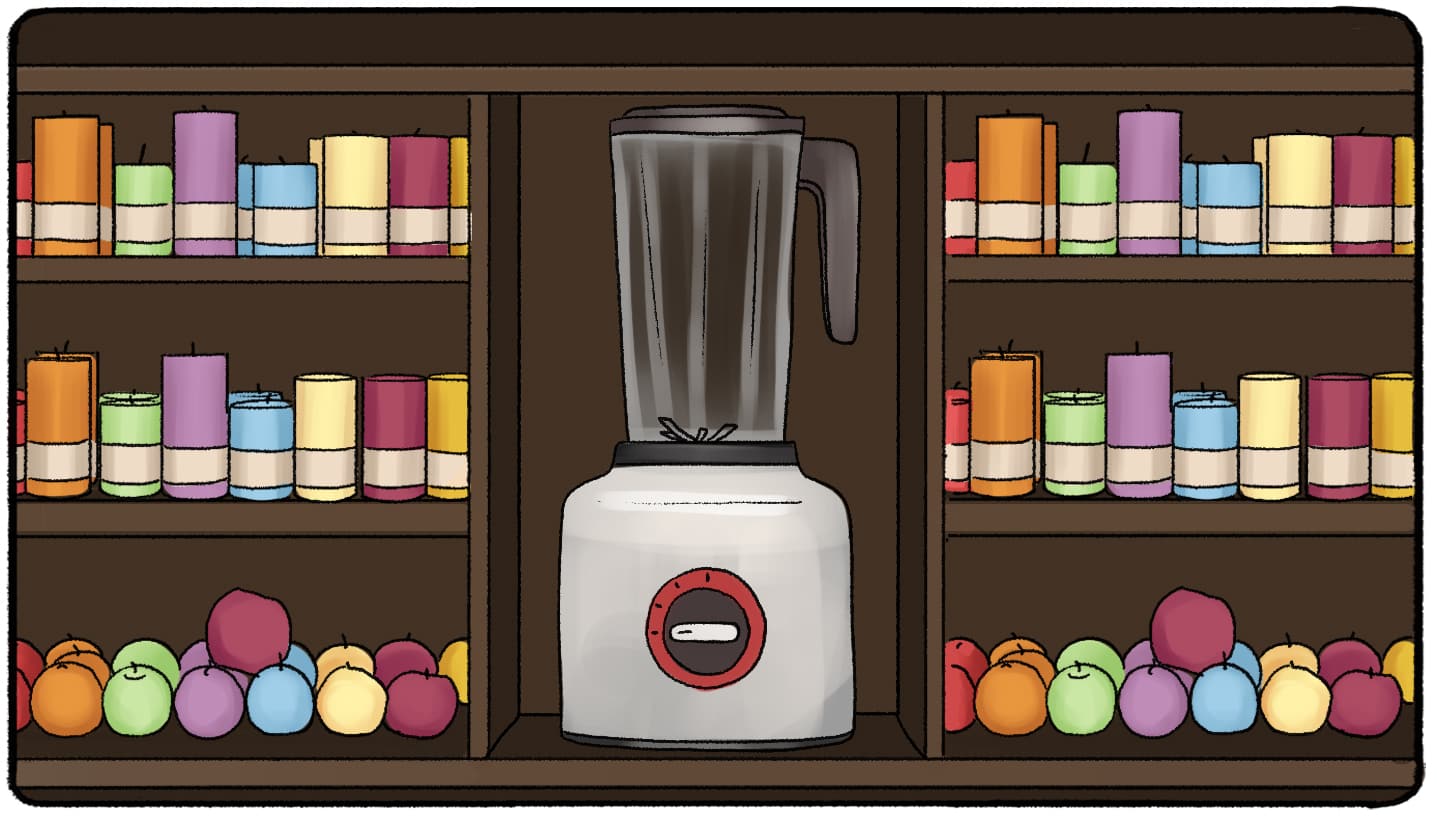
Let’s say you go into a candle store. The candle shop is stacked with the usual scents with pleasant scents. It’s only candles - except for one random blender that is also for sale. When you leave the candle store, what are you likely to remember? For many reasons, you’re most likely to remember the blender. It’s unique. It’s different. It completely takes your mind off of the pleasant-smelling candles in the store. In psychology, this is explained by the Von Restorff Effect.
What Is The Von Restorff Effect?
The Von Restorff Effect is also known as the “isolation effect.” The isolated piece of information or incident is more likely to be recalled than an event that blends into the background. When something stands out, you point your focus there, and making a solid memory begins.

In 1933, a German psychiatrist named Hedwig Von Restorff conducted experiments on memory. She discovered that when participants were given a list of generally homogenous words to remember and one very distinctive word, they were likelier to remember the distinctive word. Her study has inspired many other psychologists to look at this effect and how it affects memory.
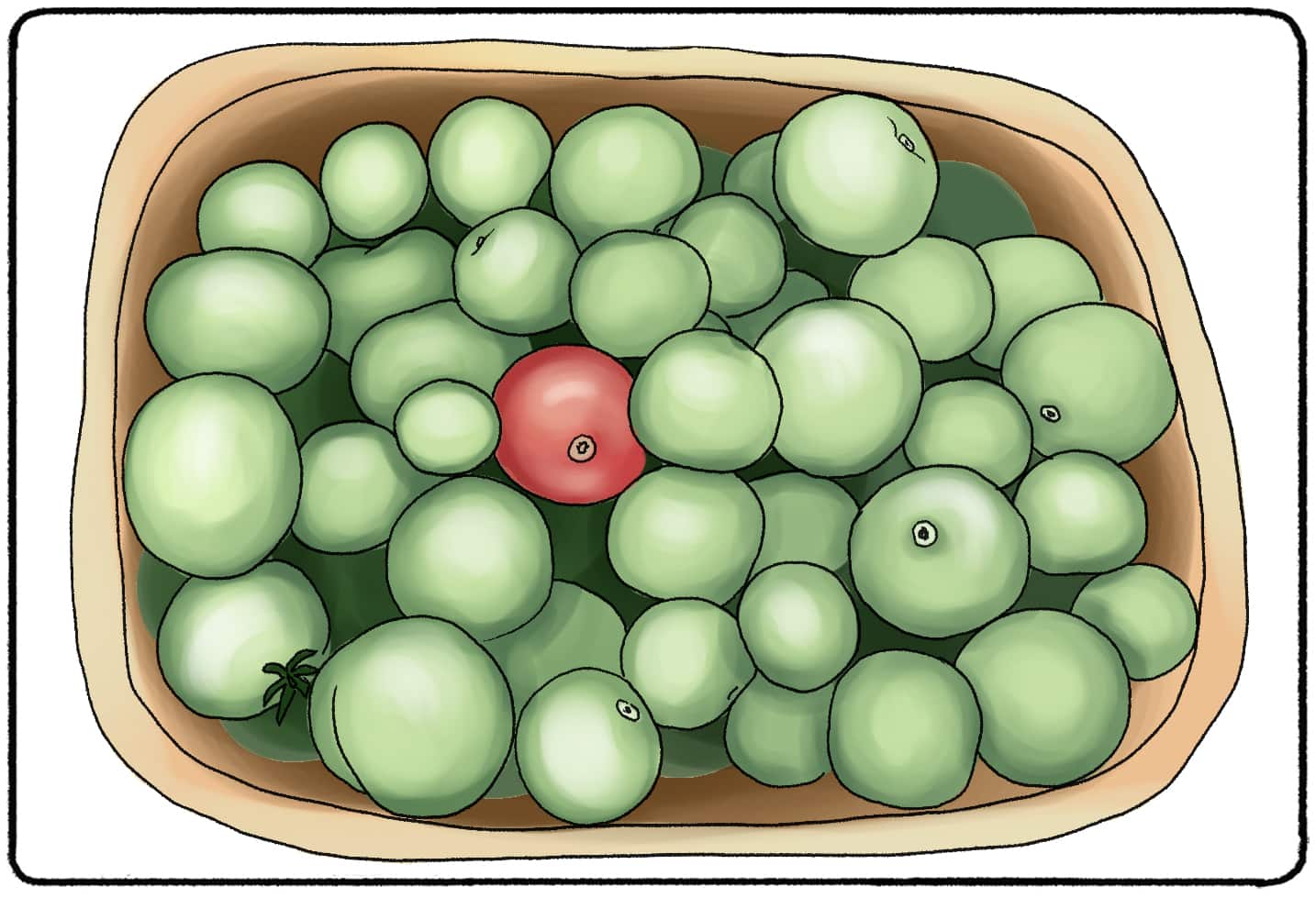
One of the most well-known images that describe the Von Restorff Effect is a photo of tomatoes. All of the tomatoes are green except for one glaringly red tomato in the middle of the photo. Even if you don’t see the photo, it’s not hard to imagine that your eyes and your focus go directly to the red tomato. And when your eyes go directly to the red tomato (and stay on that red tomato,) you are more likely to remember there was one red tomato in the basket. Unless you are asked to count the green tomatoes, you probably don't know how many are in the basket!
Is the Von Restorff Effect a Cognitive Bias?
Yes! Cognitive biases are patterns of thought that lead people to misinterpret information. That one red tomato is one of the billions of tomatoes on the Earth. It is a tomato, just like any of the green tomatoes surrounding it. So why does it stick out so much in our minds? Because cognitive biases like the Von Restorff Effect influence us.
This cognitive bias is pretty unique. Not all cognitive biases help us remember visual information. Some cognitive biases affect our judgment and decision-making, too. Examples of other cognitive biases include:
- Confirmation Bias
- Dunning-Kruger Effect
- Anchoring Bias
- Actor-Observer Bias
- Hindsight Bias
- Implicit Bias
- Ingroup and Outgroup Bias
...and many more!
How Does the Von Restorff Effect Work?
Why is our judgment affected by cognitive biases? The short answer is it takes a load off our brains! Our minds are always working hard, always taking in sights, smells, sounds, and new information. There is no way we can remember everything we see in front of us!
To make things easier, our minds take a series of shortcuts to store and recall information about the world around us. For example, if we have been in a room 1,000 times, our minds pretty much know what that room will look like. It doesn't always take in every detail, meaning we might miss small changes. (This is also known as change blindness.)
The Von Restorff Effect is just another way to make things easier for our minds. Which sounds easier: memorizing the shape, size, and placement of 100 green apples in a barrel or memorizing one red apple? See? Taking in the information that sticks out among the rest is much easier.
Elements That Produce the Von Restorff Effect
What makes information or objects stand out from the things around them? Let us count the ways! Plenty of factors can differentiate certain pieces of information on your screen, in your books, or right in front of you.
- Color
- Size
- Shape
- Motion
- Orientation
Does the Von Restorff Effect Apply to Everyone?
Although we generally store and recall memory through the same processes, age, and other factors can affect our memory ability. This led some psychologists to conduct different studies on how the Von Restorff Effect affected different ages. The studies produced exciting results. One study suggested that the Von Restorff Effect only affected the memories of children and young adults. Other studies showed that while the effect was less dramatic, older adults were also affected by the Von Restorff Effect. The elements used to make information distinct varied between studies. There is more than goes into this memory trick that meets the eye!
Examples of the Von Restorff Effect
The Von Restorff Effect, or the isolation effect, is pervasive in numerous aspects of our daily life, not just in academia. You might be unconsciously leveraging this phenomenon more often than you think!
- Highlighting in Books: You've likely used a highlighter on essential parts of a book or a document. When you glance at the page, your attention is immediately drawn to the brightly colored sections, making the highlighted information more memorable than the surrounding unmarked text.
- Unique Billboards: Think about driving on a highway filled with billboards. The one that stands out might be the one with an unusual shape, a bold color, or a catchy slogan. This distinctiveness makes it more likely that you'll recall the advertisement later.
- Fashion Choices: Ever noticed someone wearing a bright, colorful hat or shoes amidst a sea of neutral clothing? That choice of attire capitalizes on the Von Restorff Effect, making the individual more memorable in a crowd.
- Notification Badges: Many mobile apps use red notifications to indicate unread messages or updates. Amidst the regular icons on your screen, these red badges stand out, prompting you to attend to those specific apps.
- Special Sales Promotions: Retailers often use bold, contrasting colors or flashing signs for limited-time offers. This distinctiveness ensures that the promotional items grab your attention among many other products.
- Unique Ringtones: Have you ever set a specific ringtone for a particular contact? When your phone rings with that unique melody, it immediately differentiates the caller from others, making you more likely to remember who called even hours later.
Understanding and recognizing the Von Restorff Effect in these various contexts allows you to appreciate its influence on your memory and harness it effectively in various professional and personal scenarios.
How to Use the Von Restorff Effect to Remember Information
The isolation effect may harm memory. While the isolated piece of information is more likely to be remembered, the rest of the information is more likely to be forgotten. If you are trying to remember a set of information, think about what pieces stick out the most and what pieces are most important to remember. Or, you can make pieces of information stick out. Highlighting is just one way we use the isolation effect to remember critical information. There are other ways to do this, too.
- When you're writing out notes, keep two pens close. (Let's say you're using a black and blue pen.) Write most of the notes in black until you hit information that your professor says is important. When you come across important information, write it down in red.
- As you review notes, draw boxes around the information you need to remember.
- Rewrite notes after taking them as a study strategy!
UX Design and Marketing
Designers and content creators use the Von Restorff Effect all the time to help sell products and build memorable websites.
Bolded text, italic text, and text in different colors and fonts stand out. If specific messages need to reach customers, the best way to make that happen is to recruit the Von Restorff Effect and isolate those messages away from the rest of the text.
You don't have to be a UX designer or marketing expert to use the Von Restorff Effect in your messaging. If you have a message that you want to communicate to others, consider how this effect plays into your materials. Here are some quick tips for using this effect effectively!
- Consider the devices where your audience will be reading information. For example, some Kindles or other devices automatically display information in black and white. Changing the color of your text won't help users who can't see the difference! Switch up what elements you are using to make information stand out.
- Be selective with the information you want to "highlight." If every other sentence on a page stands out, nothing will stand out!
- Try A/B testing different elements of the effect. Do your users respond better when color is used to differentiate information? Size? Style? Motion?
Other UX Design Principles
Interested in designing web pages or creating a practical user experience? There are a lot of design principles, like the Von Restorff Effect, that can help you meet your goals:
- Zeigarnik Effect
- Goal-Gradient Law
- Miller's Law
- Laws of Good Gestalt (Proximity, Similarity, Closure, Symmetry, Continuity, Common Fate, Past Experience)
- Peak-End Rule
- Postel's Law
- Aesthetic-Usability Dffect
The Isolation Effect Is More Than Meets The Eye
Isolated sounds or tones of voice may also stick out enough to be more memorable. If you try a different selection of cheeses on a cheese plate, accompanied by one type of meat, you’re more likely to remember the taste of the meat. The Von Restorff Effect is not limited to just one sense or type of stimuli.
It Helps to Be Different!
The Von Restorff Effect, rooted in our inclination to remember distinct items more readily than common ones, has even been suggested by some Reddit users as a catalyst in propelling the careers of artists like Ed Sheeran and Susan Boyle. Both these performers had unique attributes that set them apart in the entertainment industry.
Ed Sheeran, with his distinctive fusion of pop, hip-hop, and folk and his raw storytelling, became a refreshing contrast to the prevailing music landscape. On the other hand, Susan Boyle defied conventional expectations on talent shows with her heartwarming rendition of "I Dreamed a Dream," surprising audiences and making her performance unforgettable.
It wasn’t just their talent but their distinctiveness that made them stand out. In an industry flooded with talent, those who differentiate themselves—be it through their style, story, or sound—are more likely to be recalled, invited back, and celebrated, while others, unfortunately, might fade into the background.

Other Ways to Remember Important Information
Understanding the idea behind the Von Restorff Effect can help you remember critical information, from essential quotes to tricky answers on your next test. But it's far from the only way to remember things! Psychologists and marketing experts have discovered other design principles and cognitive biases influencing our memories and attention. Consider the following tips if you want to remember a critical piece of information. (Full pages on these effects can all be found on this website!)
- Serial Position Effect: Want to give the most memorable speech in your class? The Primacy Effect suggests signing up to go first. The Recency Effect suggests signing up to go last! The Serial Position Effect maps out the most memorable information when presented as a series. This effect works best when presenting information in a list. Want to remember two key ingredients on your grocery list? Put them first and last!
- Change Your State of Mind: Need to memorize information for a presentation, a test, or to complete everyday tasks? Consider your state of mind. Replicate the type of environment when you need to recall information or adjust your environment when it's time to recall. If you know you'll be nervous before a speech, get your heart pumping before you memorize your information.
- Rote Memorization: Repetition is vital to memory and learning. Want to get one key message across while giving your speech? Repeat it over and over. Don't overwhelm your audience with it; repeat it enough that it becomes the most crucial message in your presentation.
- Chunking: While studying, "chunk" information into a group. Remembering one group, rather than multiple individual items, is much easier!
- Acronyms, acrostics, and more! From PEMDAS to "I before E except after C," plenty of phrases and sentences can help you remember information. Memory tricks are fun!
- Memory Palace: Visual learners might find that putting crucial information into a Memory Palace helps them recall information more effectively.
Ready, Set, Remember!
Students, designers, and anyone who wants to communicate or remember information can benefit from applying the Von Restorff Effect to their notes or communication.
